

Explore axSpA clinical manifestations in the hall of statues


LECTURE SERIES WITH DR. SAAKSHI KHATTRI
Examine the clinical manifestations of axSpA
Join Dr. Khattri as she discusses sacroiliitis and spondylitis, psoriasis, uveitis, and other axSpA manifestations and considerations to classify their SpA disease subtype.
Get to know the clinical manifestations
- Sacroiliitis and spondylitis
- Extra-musculoskeletal
- Peripheral articular
Sacroiliitis and spondylitis
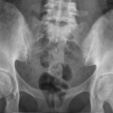
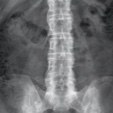
Sacroiliitis and spondylitis
Prevalence: 86%1,†
Sacroiliitis is an inflammation of one or both sacroiliac joints.2,3
Spondylitis is an inflammation in the insertion of tendons and ligaments into bone with contiguous inflammation of the substance of vertebral bone.2,3
Both features manifest symptomatically as insidious inflammatory back pain, with onset at age <40 years, which improves with exercise but not with rest, and can include pain at night.3
†Sacroiliitis on MRI.
Image copyright courtesy of Dr Lýdia Priskin, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 36996 Case courtesy of Dr Hani Makky Al Salam, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 9152
Extra-musculoskeletal
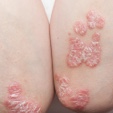
Psoriasis
Prevalence: 13%1
An auto-immune skin disease that features red, itchy, scaly skin on the9:
- Knees
- Elbows
- Trunk
- Scalp
Psoriasis can be a manifestation of axSpA. It is unclear whether this form of disease should be classified as axSpA with psoriasis or as PsA with axial involvement (axial PsA). However, minor differences distinguish these two disease states: patients with axSpA and psoriasis tend to present with fewer peripheral symptoms and are more commonly HLA-B27 positive than patients with axial PsA.10
Extra-musculoskeletal
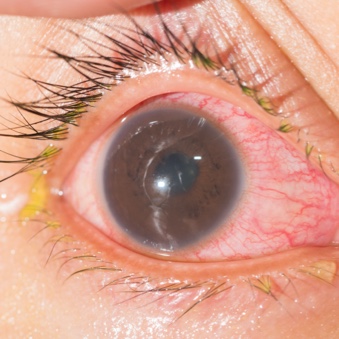
Acute anterior uveitis
Prevalence: 16%–37%4,5
A non-infectious acute inflammation of the anterior uveal tract.6
Symptoms6:
- Eye redness and pain
- Floaters
- Photophobia
- Blurry vision
Acute anterior uveitis in axSpA presents as singular, anterior, and unilateral flares that can last up to 3 months.7 The prevalence of AAU increases with disease duration, and recurrent or untreated AAU can lead to glaucoma, cataracts, and vision loss, which significantly impact quality of life.8
AAU= acute anterior uveitis.
Extra-musculoskeletal
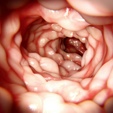
IBD
Prevalence: 5%1
Chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract may be observed.11
Symptoms include12:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Rectal bleeding
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
IBD=inflammatory bowel disease.
Peripheral articular
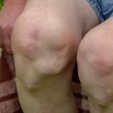
Peripheral arthritis
Prevalence: 15%–58%4,15
Arthritis of peripheral joints, which is found predominately in the lower limbs of patients.15 A recent study found that 65.9% of patients with axSpA showed a first episode of peripheral arthritis after axial involvement, so ongoing monitoring is needed in these patients.15
Peripheral articular
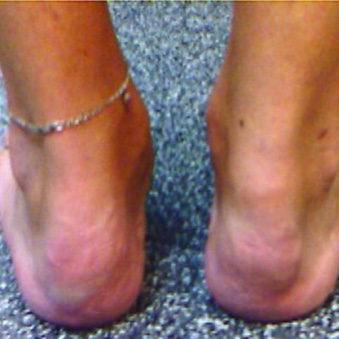
Enthesitis
Prevalence: 34%–74%14
Inflammation at the insertion point of ligaments, tendons, or joint capsules into bone, with the heel (either the location of the insertion of the Achilles tendon or the plantar fascia) being the most frequent first location affected and causing pain.13
Image copyright: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/enthesitis-of-the-Achilles-tendon-Note-arrows-indicate-severe-inflamation-of-the_fig3_305322505
Peripheral articular
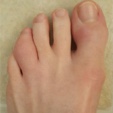
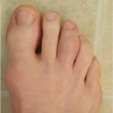
Dactylitis
Prevalence: 6%–8%4,13
Digit inflammation leading to swelling, which occurs more frequently in the feet than in the hands; however, recent research suggests this may vary by subtype of SpA.13
Image copyright https://www.the-rheumatologist.org/article/case-report-a-psoriasis-arthritis-patient-with-dactylitis-enthesits/?singlepage=1
Important distinctions are emerging about which cytokines contribute to various clinical manifestations


NEXT ROOM IN THE MANIFESTATIONS EXHIBIT
Burden of disease
Understand the axSpA burden of disease and the impact on patients’ quality of life.
PREVIOUS ROOM
Clinical features
Become a member of the RheuMuseum and be the first to know about new exhibits
- van den Berg R, de Hooge M, van Gaalen F, et al. Percentage of patients with spondyloarthritis in patients referred because of chronic back pain and performance of classification criteria: experience from the spondyloarthritis caught early (SPACE) cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(8):1492-1499. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ket164
- Sieper J, Braun J, Dougados M, et al. Axial spondyloarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15013
- Garg N, van den Bosch F, Deodhar A. The concept of spondyloarthritis: where are we now? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(5):663–672. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2014.10.007
- de Winter JJ, van Mens LJ, van der Heijde D, et al. Prevalence of peripheral and extra-articular disease in ankylosing spondylitis versus non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):196. doi:10.1186/s13075-016-1093-z
- Roche D, Badard M, Boyer L, et al. Incidence of anterior uveitis in patients with axial spondyloarthritis treated with anti-TNF or anti-IL17A: a systematic review, a pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):192.
- Guly CM, Forrester JV. Investigation and management of uveitis. BMJ. 2010;341:c4976. Published 2010. doi:10.1136/bmj.c4976
- Rademacher J, Poddubnyy D, Pleyer U. Uveitis in spondyloarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020;12:1759720X20951733. Published 2020. doi:10.1177/
- van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van Bentum RE, Verbraak FD, et al. Reduction of anterior uveitis flares in patients with axial spondyloarthritis on certolizumab pegol treatment: final 2-year results from the multicenter phase IV C-VIEW study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13:1759720X211003803.
- Meier K, Schloegl A, Poddubnyy D, Ghoreschi K. Skin manifestations in spondyloarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020;12:1759720X20975915. Published 2020. doi:10.1177/1759720X20975915
- Benavent D, Plasencia-Rodríguez C, Franco-Gómez K, et al. Axial spondyloarthritis and axial psoriatic arthritis: similar or different disease spectrum? Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020;12:1–8. doi: 10.1177/1759720X20971889.
- Fragoulis GE, Liava C, Daoussis D, et al. Inflammatory bowel diseases and spondyloarthropathies: From pathogenesis to treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(18):2162-2176. doi:10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2162
- CDC. What is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)? - inflammatory bowel disease - division of Population Health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/what-is-IBD.htm. Page last reviewed: April 13, 2022. Accessed October 19, 2022
- López-Medina C, Molto A, Sieper J, et al. Prevalence and distribution of peripheral musculoskeletal manifestations in spondyloarthritis including psoriatic arthritis: results of the worldwide, cross-sectional ASAS-PerSpA study. RMD Open. 2021;7(1):e001450. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001450
- Mease PJ, Liu M, Rebello S, et al. Characterization of patients with axial spondyloarthritis by enthesitis presence: data from the Corrona Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondyloarthritis Registry. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020;7:449-456.
- López-Medina C, Dougados M, Ruyssen-Witrand A, et al. Evaluation of concomitant peripheral arthritis in patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis: 5-year results from the DESIR cohort. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):139. Published 2019. doi:10.1186/s13075-019-1927-6